Modeling of Droplet Charge Dynamics During an Ink Jet Breakup Using COMSOL Multiphysics®
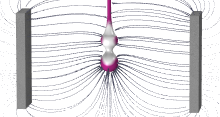
Continuous Ink Jet (CIJ) printing technologies are widely used in the field of industrial coding and marking. These technologies are based on the emission of a high-speed jet of ink droplets (20 m/s) onto the surface of a moving medium. To maintain sufficient print quality, it is essential to control the positions of the droplets on the printing medium. The position of each droplet depends on several factors, including the quality of the jet breakup, the charge carried by each droplet, the deflection of the droplets in an electric field, and their interactions in flight. Numerical modelling can provide detailed information at each step, allowing to predict the behaviour of ink droplets, and ultimately helping to design CIJ printheads. This article focuses on modelling the droplet charging process between electrodes during ink jet breakup in the COMSOL Multiphysics® software. The dynamics of the ink jet surrounded by air is modelled using the Two-Phase Flow, Level Set coupling feature from the CFD Module. The spatial charge is modelled using the Electric Currents (EC) physics interface from the AC/DC Module. With a particular attention to the timestep, numerical simulations can be used to predict the charge embedded in each droplet just before the breakup, and therefore the embedded charge in each droplet that is deflected after breakup. This model also allows to apprehend the historical charge distributed along the following droplets. The prediction of the uncharged jet breakup dynamics is assessed thanks to experiments run at MARKEM-Imaje, validating the CFD part of the model, and providing confidence in using the charging model for industrial use.