Multiphysics Method for Short Circuit Stress Calculation in Power Transformer
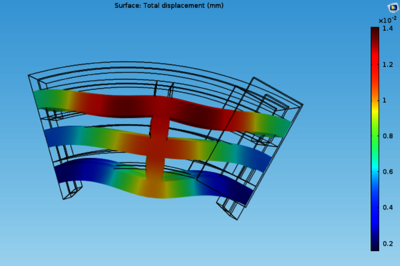
The aim of this work is to compute the mechanical stresses in power transformer winding due to an external short-circuit event. This event can be considered as one of the most demanding load conditions and many details such as material type, type of constraints, winding geometry influence system behavior. Design parameters which determine the maximum stresses in the windings are part of the work. A Multiphysics approach was used between electromagnetic and structural analysis. A parametrized geometry 2D axisymmetric was used to compute the Lorentz forces, in particular, the Magnetic Fields interface of the AC/DC Module was used to compute magnetic field and induced current distributions in and around the windings, in this way is possible to obtain the exact Lorentz forces distribution (radial and axial). The forces calculated in this way are passed by a General Extrusion operator from a 2D axisymmetric component to a 3D component in Solid Mechanics interface in which the symmetry of the winding are used and the actual stress values reached are calculated after the mechanical constraints of the system have been set. The results obtained showing a very good comparison with the traditional analytical formula. The use of the COMSOL Multiphysics® to study this phenomena allows:
- Build a parameterized geometrical
- Use a detailed 2D axisymmetric model to achieve skin and proximity effect on the conductors
- Easy coupling between the electromagnetic and structural model